- Home
- Curriculum and Exams
- Subjects
- Computer Science
Computer Science
BackHead of Department: Mr C Humphrey
Teachers: Miss T Green, Mr S Hamilton, Mr G Roberts, Mr C Scott, Mr M Smith
Technicians:
Tunbridge Wells: Mr T Bance, Mr J Large, Mr C Marks
Sevenoaks: Mr A Collins, Mr D Conway
The Computer Science department is a forward-looking department that looks at changes within computers and other technologies. We spend time examining the impact that technology has on individuals and communities, as well as teaching and improving students' skills and understanding of the subject. We provide opportunities for students to study Computer Science at GCSE and at A Level. [Updated 2025/26]
Computers are incredibly fast, accurate and stupid; humans are incredibly slow, inaccurate and brilliant; together they are powerful beyond imagination.
(Albert Einstein)
Years 7, 8 and 9
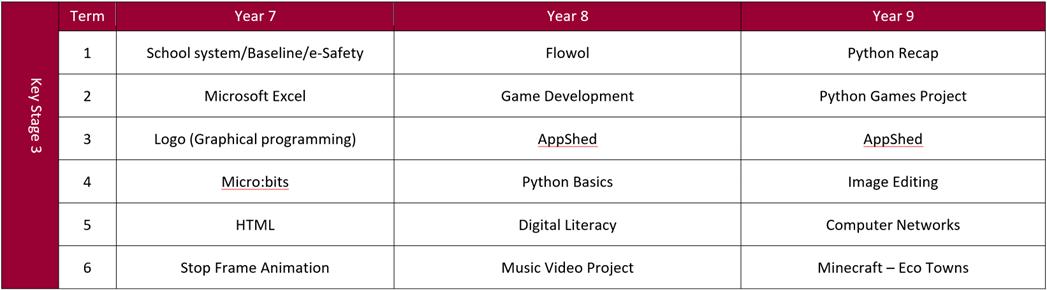
Year 7
Students look at basic skills and move on to LOGO and basic computational thinking and problem solving. We also show the students how to program a small, single board computer. Other topics covered are HTML and Microsoft Excel.
Year 8
Students in Year 8 look at developing an app for use on a phone/tablet. We also spend time exploring flow charts and their uses; and we introduce the Python Programming Language, which enables the students to solve simple problems using their programming skills.
Year 9
Year 9 students spend time revising their programming knowledge and then move on to developing their own project, based around simple games. We look at image editing and computer networks and round off the year looking at the idea of sustainable towns and buildings using Minecraft as a teaching tool.
GCSE: Years 10 and 11
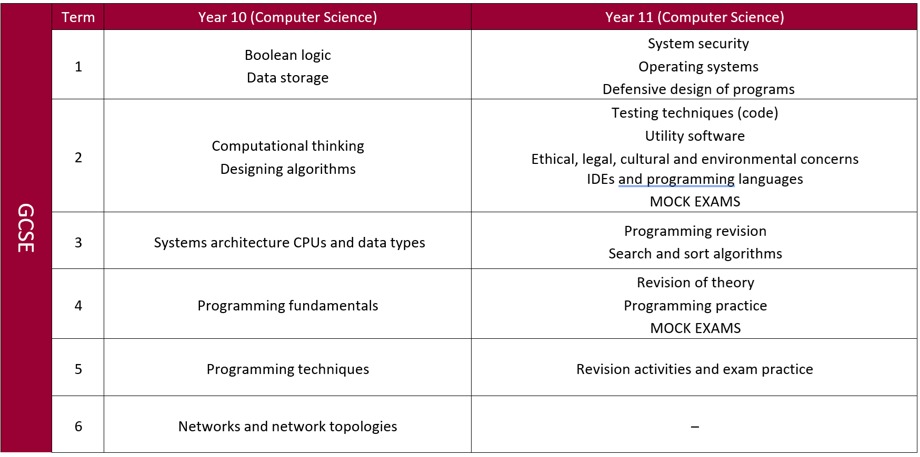
Course content
The qualification will build on the knowledge, understanding and skills established through the Computer Science elements of the Key Stage 3 programme of study. The content has been designed not only to allow for a solid basis of understanding but to engage learners and get them thinking about real world application. The new specification will enable learners to develop computational thinking skills built on a sound base of conceptual learning and understanding. They will analyse problems in computational terms through practical experience of solving such problems, including designing, writing and debugging programs.
Assessment/examination
Two written papers (1½ hours each)
Exam board: OCR
A Level: Years 12 and 13
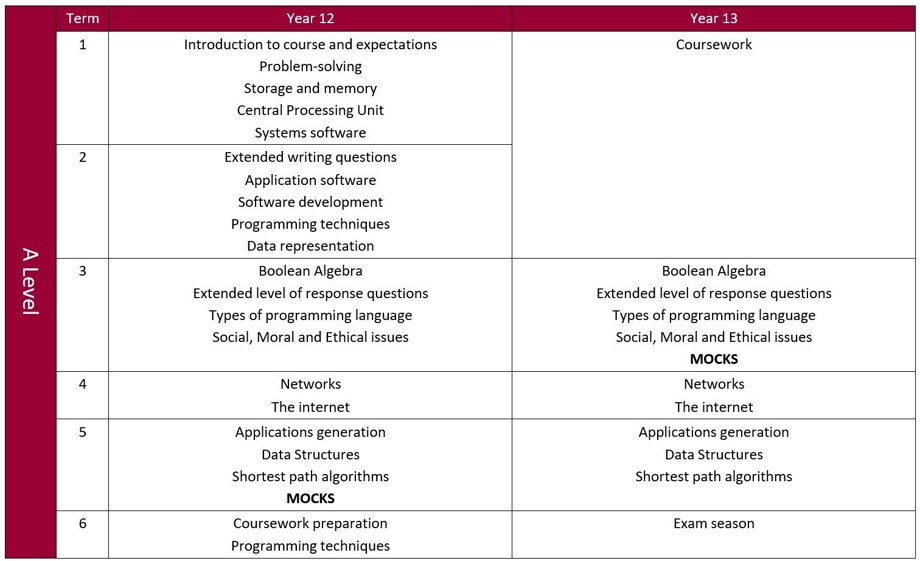
The course focuses on programming, building on the GCSE Computing and emphasises the importance of computational thinking as a discipline. It has an expanded maths focus, much of which is embedded within the course. It has computational thinking at its core, helping students to develop the skills to solve problems, design systems and understand human and machine intelligence – a valuable transferrable skill. It allows students to apply the academic principles learned in the classroom to real-world systems in an exciting and engaging manner.
It will give students a clear progression into higher education, as the course was designed after consultation with members of BCS, CAS and top universities.
Assessment/examination
80% exam (two written exam papers 2½ hours each)
20% programming coursework
Exam board: OCR
Careers Education
Computer Science teaches students how to approach complex problems methodically and find efficient solutions. Students also gain hands-on experience with coding, software development and understanding algorithms. This practical knowledge is directly applicable to many job roles in the tech industry, such as software engineering, data analysis, and IT support. Students spend time learning how to approach complex problems methodically and find efficient solutions. These skills are highly valued in many industries – from technology to finance – and are essential for success in higher education.
